Coding and Non-Coding Variation in 74 Novel Full-Length Sequences of KIR2DL1
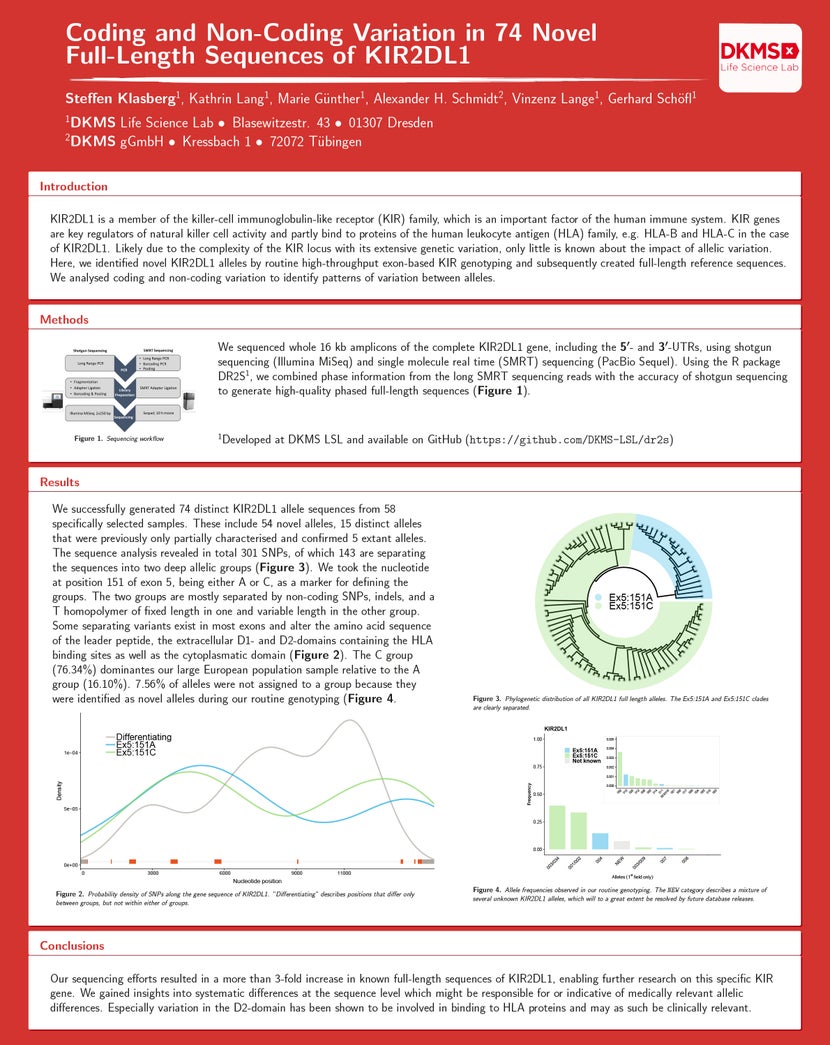
KIR2DL1 is a member of the killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family, which is an important factor of the human immune system. KIR genes are key regulators of natural killer cell activity and partly bind to proteins of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) family, e.g. HLA-B and HLA-C in the case of KIR2DL1. Likely due to the complexity of the KIR locus with its extensive genetic variation, only little is known about the impact of allelic variation. Here, we identified novel KIR2DL1 alleles by routine high-throughput exon-based KIR genotyping and subsequently created full-length reference sequences. We analysed coding and non-coding variation to identify patterns of variation between alleles.
Details
Authors
Steffen Klasberg, Kathrin Lang, Marie Günther, Alexander H. Schmidt, Vinzenz Lange, Gerhard Schöfl
Publishing Date
01/10/2018
Category
Bioinformatics Research, Genotyping