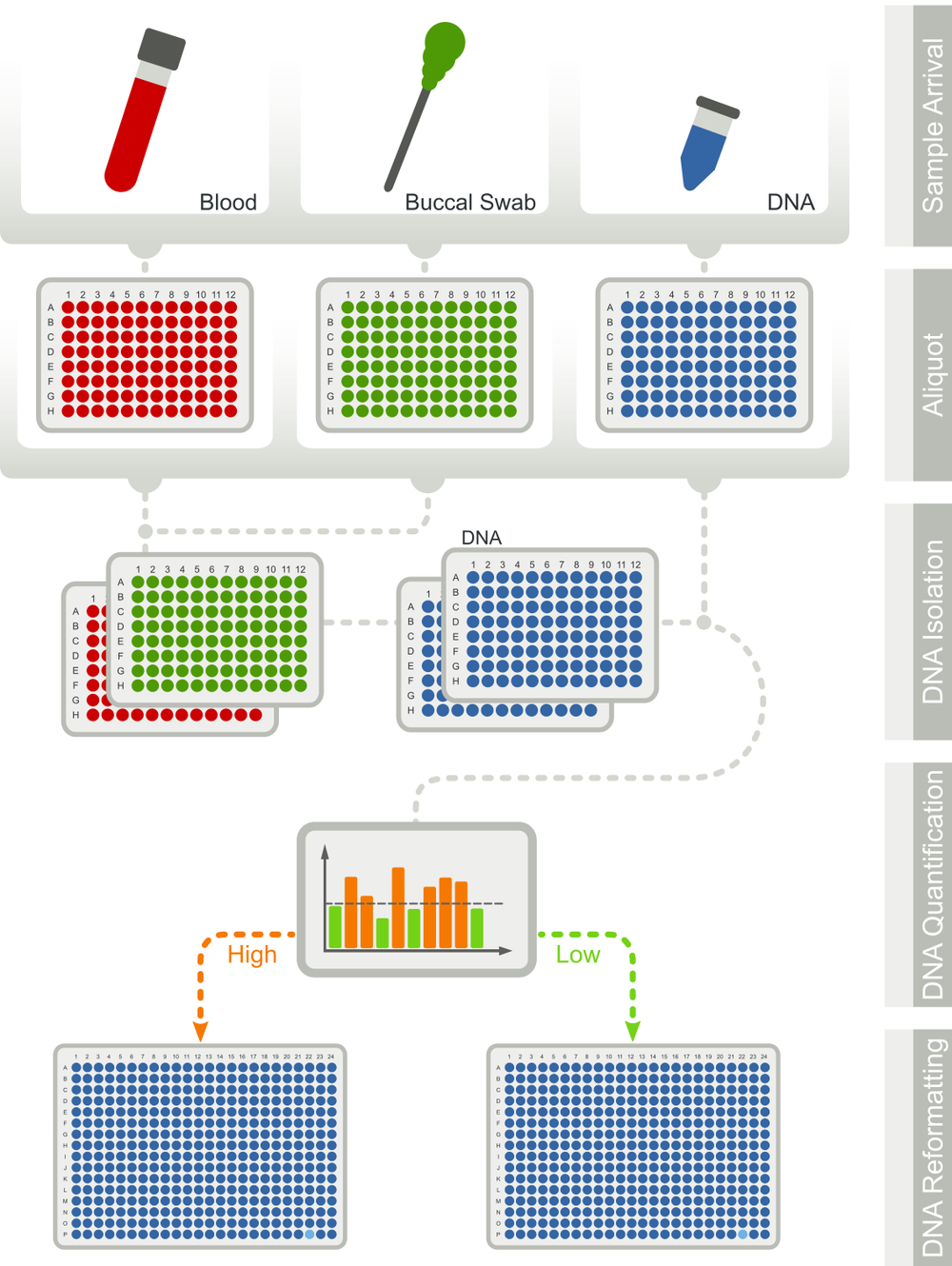
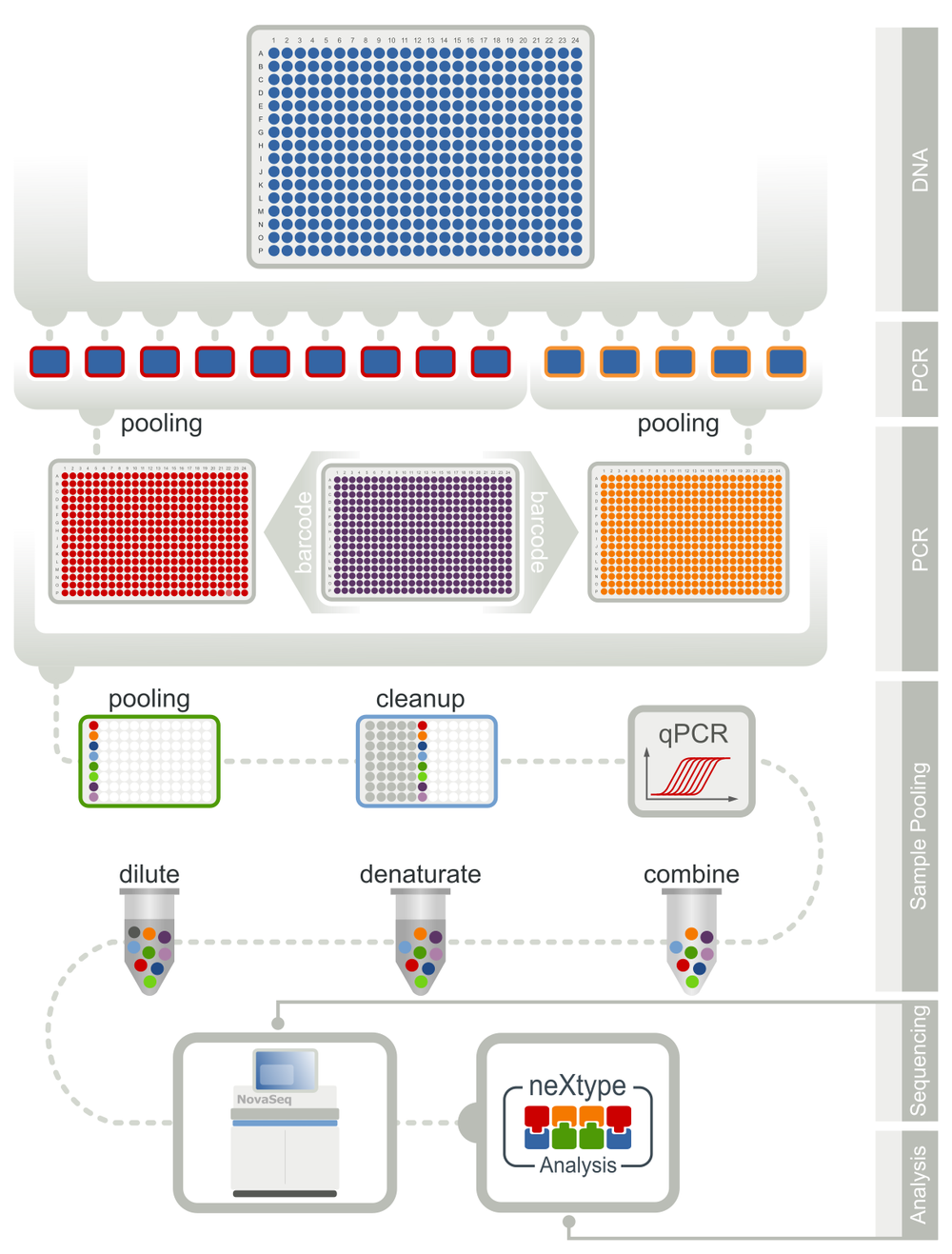
High-throughput HLA Genotyping Workflow
For the genotyping of over one million potential stem cell donors per year, we developed a highly automated workflow with the largest genotyping profile worldwide. Thus, we do not only report mandatory genes but also genes, whose relevance is still an ongoing discussion in the scientific community (e.g. HLA-E, MICA/B, KIR). By providing pre-genotyped donors for these genes, we facilitate further studies, which will hopefully lead to an improved donor selection in the future.